Sensational Tips About How To Debug In Inspect Source
Debugging with Inspect Source
1. Unlocking the Secrets Hidden in Your Browser
Ever felt like your website is speaking a language you don't understand? Maybe a button isn't clicking, a form isn't submitting, or something just looks plain wonky. Fear not, intrepid web adventurer! The "Inspect Source" tool, tucked away in your browser, is your trusty magnifying glass for deciphering the mysteries of web code. It's like having X-ray vision for websites, allowing you to peek behind the curtain and see what's really going on.
Think of it as debugging in Inspect Source is like being a detective. You've got a problem (a bug!), and you need to follow the clues to find the culprit. These clues are the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code that make up the website. Inspect Source lets you examine this code in real-time, see how it's interacting, and even make changes to test your theories.
But where do you even begin? That's what we're here to explore. This isn't about becoming a coding wizard overnight; it's about equipping you with the basic skills to understand what's happening under the hood and to effectively communicate with developers when things go sideways (which, let's be honest, they often do).
So, grab your metaphorical trench coat and notepad, and let's dive into the world of Inspect Source! We'll cover the basics, some handy tricks, and how to use it to solve common web problems. Prepare to become a web-debugging extraordinaire!
Getting Started
2. Opening the Door to Web Insights
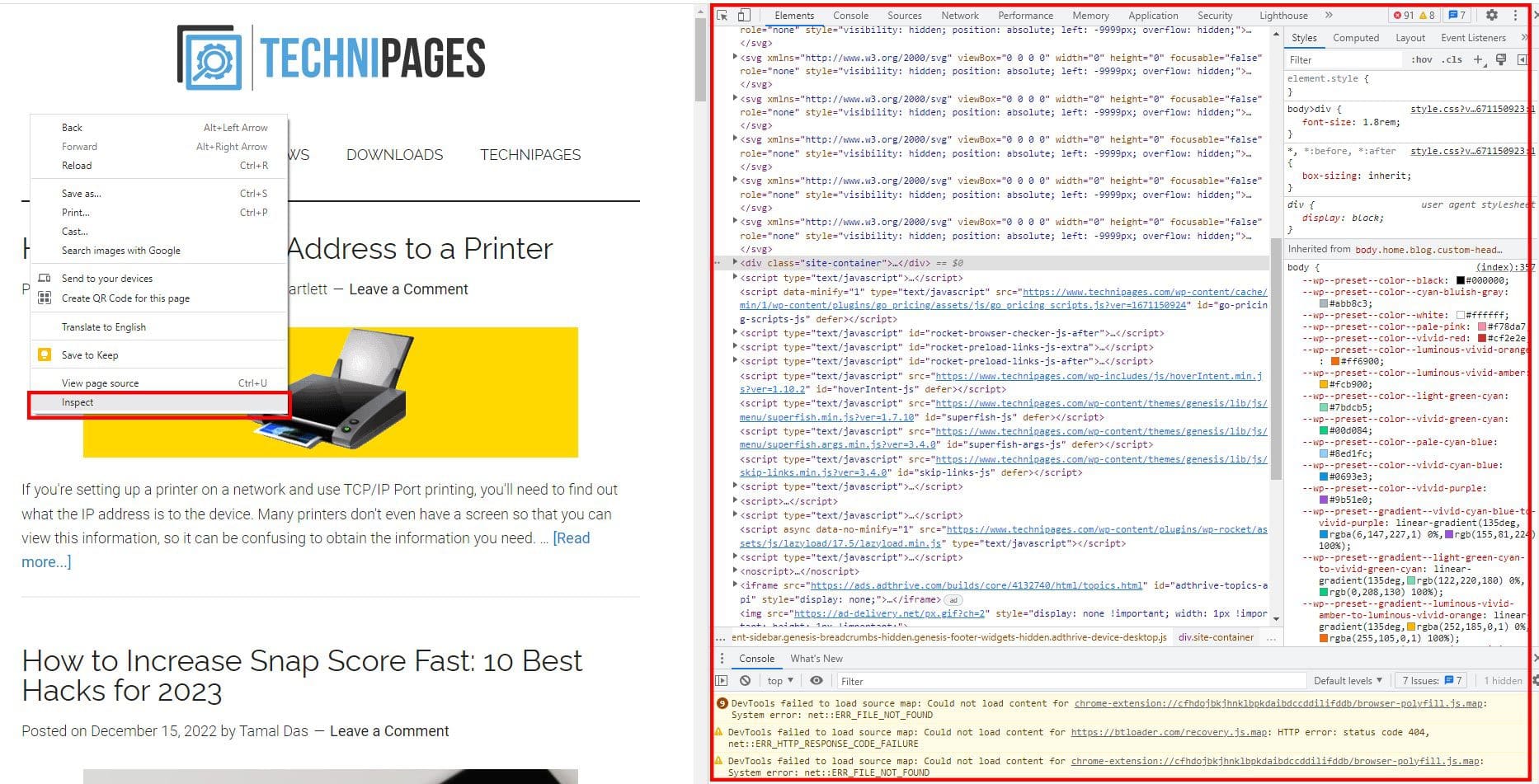
Accessing Inspect Source is usually pretty straightforward. In most browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari), you can right-click anywhere on a webpage and select "Inspect" or "Inspect Element." Alternatively, you can use keyboard shortcuts: Ctrl+Shift+I (or Cmd+Option+I on Mac) or simply press F12. Poof! A panel will appear, usually at the bottom or side of your browser window, revealing the webpage's inner workings.
Now, brace yourself — you're looking at code! Don't panic! The main tabs you'll likely use are "Elements" and "Console." "Elements" shows the HTML structure of the page, allowing you to navigate through the different parts of the website's content. It's like looking at the skeleton of the webpage. You can click on different elements to see their corresponding code, and you can even edit the code directly to see how changes affect the page in real-time. Be careful though, these changes are only temporary and will disappear when you refresh the page.
The "Console" is where JavaScript errors and messages pop up. Think of it as the website's error log. If something isn't working right, chances are there's an error message in the Console giving you a hint about what went wrong. It's also a place where developers can write JavaScript code to test things out or debug their scripts. Don't worry if it looks like gibberish at first; we'll get into some common errors later on.
Beyond those two, you might find "Network" useful. This tab shows all the files (images, CSS, JavaScript) that the webpage is loading. It can help you identify if a file is missing or taking too long to load, which can impact performance. The "Sources" tab is a powerful tool for advanced debugging of JavaScript code, allowing you to set breakpoints and step through the code line by line. But for now, let's stick with the Elements and Console tabs to keep things manageable.
How To Debug WebAssembly Pipelines In Your Web Browser
Finding and Fixing Common Errors
3. Decoding the Language of Bugs
Okay, so you've got Inspect Source open, and you see an error in the Console. What now? The good news is that many errors are fairly common, and understanding them can save you a lot of head-scratching. One frequent offender is a "404 Not Found" error. This usually means that a file the webpage is trying to load (like an image or a CSS file) is missing or the URL is incorrect. Double-check the URL in the "Network" tab to make sure it's pointing to the right place. It is also an indication that the server the file is located in has an issue.
Another common error is related to JavaScript. You might see something like "Uncaught ReferenceError: variable is not defined." This means that your JavaScript code is trying to use a variable that hasn't been declared. It could be a typo in the variable name, or it could be that the variable is defined in a different part of the code that hasn't been loaded yet. Check the JavaScript code carefully for any misspellings or missing declarations.
CSS can also cause problems. If something isn't displaying correctly on the page, it could be a CSS issue. Use the "Elements" tab to inspect the element that's not behaving, and look at the CSS styles that are being applied to it. You can even temporarily disable or modify styles to see how it affects the appearance of the page. This is a great way to pinpoint which CSS rule is causing the problem.
Remember, the error messages in the Console are your friends! They might seem cryptic at first, but they often provide valuable clues about what's going wrong. Google is also your friend! Copy and paste the error message into Google search, and you'll likely find someone else who has encountered the same problem and found a solution. Don't be afraid to ask for help online; the web development community is generally very helpful and supportive.
Debug Add Ins On Windows Using Visual Studio Code And Microsoft Edge
Advanced Techniques
4. Unleash Your Inner Web Developer
One of the coolest things about Inspect Source is that you can actually edit the HTML and CSS of a webpage directly in your browser. This is incredibly useful for experimenting with different layouts, styles, and content without having to make changes to the actual website files (yet!). Just remember that these changes are temporary and will disappear when you refresh the page.
To edit an HTML element, simply right-click on it in the "Elements" tab and select "Edit as HTML." You can then modify the code directly, and the changes will be reflected on the page in real-time. You can add, remove, or modify any HTML attribute or content. This is a great way to test out different layouts or try out new content ideas.
Similarly, you can edit CSS styles in the "Elements" tab. When you select an element, you'll see the CSS styles that are being applied to it in the "Styles" pane. You can click on any style to edit its value, or you can add new styles altogether. This is a powerful way to experiment with different visual designs and see how they affect the appearance of the page. You can change colors, fonts, sizes, and more, all without touching the actual CSS files.
These editing capabilities are not just for fun and games! They are incredibly valuable for debugging and troubleshooting. By making temporary changes to the code, you can quickly identify which parts of the code are causing problems. You can also use these techniques to test out different solutions and see if they work before making permanent changes to the website. Just remember to keep track of the changes you make, so you can apply them to the actual website files later on.
Working with JavaScript
5. Taming the Wild West of Interactive Code
JavaScript adds interactivity and dynamic behavior to webpages. It's what makes things move, change, and respond to user actions. But JavaScript can also be tricky to debug, especially when dealing with complex interactions and asynchronous operations. Inspect Source provides several tools to help you debug JavaScript code effectively. You can use the "Console" tab to log messages, the "Sources" tab to set breakpoints, and the "Debugger" to step through the code line by line.
Logging messages to the Console is a simple but powerful debugging technique. You can use the `console.log()` function to output values, variables, and messages to the Console at different points in your code. This allows you to see what's happening at each step and identify where things are going wrong. For example, you can log the value of a variable before and after it's modified to see if it's changing as expected.
Breakpoints are markers that you can set in your JavaScript code to pause execution at specific lines. When the code reaches a breakpoint, the debugger will stop and allow you to inspect the current state of the program. You can then step through the code line by line, examine the values of variables, and see how the code is executing. This is incredibly useful for understanding complex logic and identifying the root cause of bugs.
The "Debugger" tool in Inspect Source allows you to step through your JavaScript code line by line, execute code snippets, and examine the call stack. It provides a detailed view of the program's execution and helps you understand how different parts of the code interact. The Debugger can be daunting at first, but with a little practice, it becomes an indispensable tool for debugging JavaScript code.
How To Inspect WebViews For App Debugging Sertaç ARTUN's Blog
FAQ
6. Demystifying the Tool for Everyone
Let's tackle some common questions about using Inspect Source. No question is too basic! We all start somewhere.
7. Q
A: Nope! Any changes you make are temporary and only visible to you in your browser. When you refresh the page, everything goes back to normal. It's like a sandbox environment for experimenting.
8. Q
A: Absolutely not! While developers use it extensively, anyone can benefit from learning the basics of Inspect Source. It's a great tool for understanding how websites work, troubleshooting problems, and communicating effectively with developers.
9. Q
A: While you can view the code, simply copying and pasting someone else's design is generally not cool and might even infringe on copyright. Use Inspect Source as a learning tool and for inspiration, but always create your own unique designs and respect intellectual property.